lv heave | heaves and thrills palpation lv heave A sustained thrust at the apex (easily differentiated from the less focal, somewhat diffuse precordial heave of RV hypertrophy) suggests LV hypertrophy. Abnormal focal systolic impulses in the precordium can sometimes be felt in patients . $10K+
0 · right ventricular heave meaning
1 · precordium pulsations and heave assessment
2 · precordium heave or lift
3 · parasternal heave vs thrill
4 · left ventricular heave
5 · how to palpate for thrills
6 · heaves and thrills palpation
7 · heaves and thrills cardiac exam
Oyster, 40 mm, Oystersteel. Oyster architecture. Monobloc middle case, screw-down case back and winding crown. Diameter. 40 mm. Material. Oystersteel. Bezel. Smooth. Winding crown. Screw-down, Twinlock double waterproofness system. Crystal. Scratch-resistant sapphire. Water resistance. Waterproof to 100 metres / 330 feet
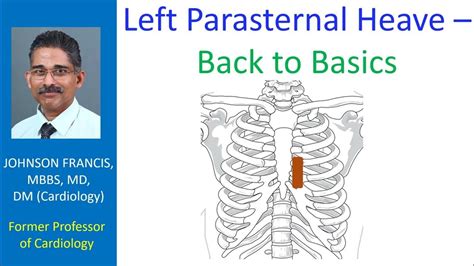
Left lower parasternal palpation (heave) Located at the left parasternal intercostal spaces 3 & 4 .A parasternal heave, lift, or thrust is a precordial impulse that may be felt (palpated) in patients with cardiac or respiratory disease. Precordial impulses are visible or palpable pulsations of the chest wall, which originate on the heart or the great vessels.A sustained thrust at the apex (easily differentiated from the less focal, somewhat diffuse precordial heave of RV hypertrophy) suggests LV hypertrophy. Abnormal focal systolic impulses in the precordium can sometimes be felt in patients . This video demonstrates assessment for parasternal heave and thrills, which is .
Left lower parasternal palpation (heave) Located at the left parasternal intercostal spaces 3 & 4 May be normal in children or small/thin adults but if present throughout systole, then likely pathologic and suggestive of right ventricular hypertrophyA parasternal heave, lift, [1] or thrust [2] is a precordial impulse that may be felt (palpated) in patients with cardiac or respiratory disease. Precordial impulses are visible or palpable pulsations of the chest wall, which originate on the heart or the great vessels.A sustained thrust at the apex (easily differentiated from the less focal, somewhat diffuse precordial heave of RV hypertrophy) suggests LV hypertrophy. Abnormal focal systolic impulses in the precordium can sometimes be felt in patients with a dyskinetic ventricular aneurysm. This video demonstrates assessment for parasternal heave and thrills, which is done as part of a cardiology examination.
Left parasternal heave is a systolic elevation of left costal cartilages due to contraction of a hypertrophied right ventricle. In the early nineteen sixties, a device was available to record the precordial impulse – both apical and parasternal and the recording was called impulse cardiogram [1].: https://johnsonfrancis.org/professional/what-is-left-parasternal-heave/ What is left parasternal heave?Left parasternal heave is a systolic elevation of left costal cartilages due to contraction of a hypertrophied right ventricle. In the early nineteen sixties, a device was .more. Left .
A parasternal heave is detected by placing the heel of the hand over the left parasternal region. In the presence of a heave the heel of the hand is lifted off the chest wall with each systole. A parasternal heave is caused by: right ventricular enlargement, or; rarely, severe left atrial enlargement which pushes the right ventricle forwards A parasternal heave is detected by placing the heel of the hand over the left parasternal region. In the presence of a heave the heel of the hand is lifted off the chest wall with each systole. A parasternal heave is caused by: right ventricular enlargement, or; rarely, severe left atrial enlargement which pushes the right ventricle forwards left ventricular heave, forceful apex beat; loud aortic second heart sound; signs of underlying cause; Management: seek expert advice; patients with LVH should be identified as it increases the risk of developing a myocardial infarction with a level of hypertension that would not normally be indicative for treatment
Left lower parasternal palpation (heave) Located at the left parasternal intercostal spaces 3 & 4 May be normal in children or small/thin adults but if present throughout systole, then likely pathologic and suggestive of right ventricular hypertrophyA parasternal heave, lift, [1] or thrust [2] is a precordial impulse that may be felt (palpated) in patients with cardiac or respiratory disease. Precordial impulses are visible or palpable pulsations of the chest wall, which originate on the heart or the great vessels.A sustained thrust at the apex (easily differentiated from the less focal, somewhat diffuse precordial heave of RV hypertrophy) suggests LV hypertrophy. Abnormal focal systolic impulses in the precordium can sometimes be felt in patients with a dyskinetic ventricular aneurysm. This video demonstrates assessment for parasternal heave and thrills, which is done as part of a cardiology examination.

right ventricular heave meaning
Left parasternal heave is a systolic elevation of left costal cartilages due to contraction of a hypertrophied right ventricle. In the early nineteen sixties, a device was available to record the precordial impulse – both apical and parasternal and the recording was called impulse cardiogram [1].: https://johnsonfrancis.org/professional/what-is-left-parasternal-heave/ What is left parasternal heave?Left parasternal heave is a systolic elevation of left costal cartilages due to contraction of a hypertrophied right ventricle. In the early nineteen sixties, a device was .more. Left . A parasternal heave is detected by placing the heel of the hand over the left parasternal region. In the presence of a heave the heel of the hand is lifted off the chest wall with each systole. A parasternal heave is caused by: right ventricular enlargement, or; rarely, severe left atrial enlargement which pushes the right ventricle forwards
A parasternal heave is detected by placing the heel of the hand over the left parasternal region. In the presence of a heave the heel of the hand is lifted off the chest wall with each systole. A parasternal heave is caused by: right ventricular enlargement, or; rarely, severe left atrial enlargement which pushes the right ventricle forwards


prada sunglasses 270s
precordium pulsations and heave assessment
Chanel No. 5 was the first perfume launched by French couturier Gabrielle "Coco" Chanel in 1921. The scent formula for the fragrance was compounded by French-Russian chemist and perfumer Ernest Beaux. The design of its bottle has been an important part of the product's branding.
lv heave|heaves and thrills palpation

























